Blog
Technology
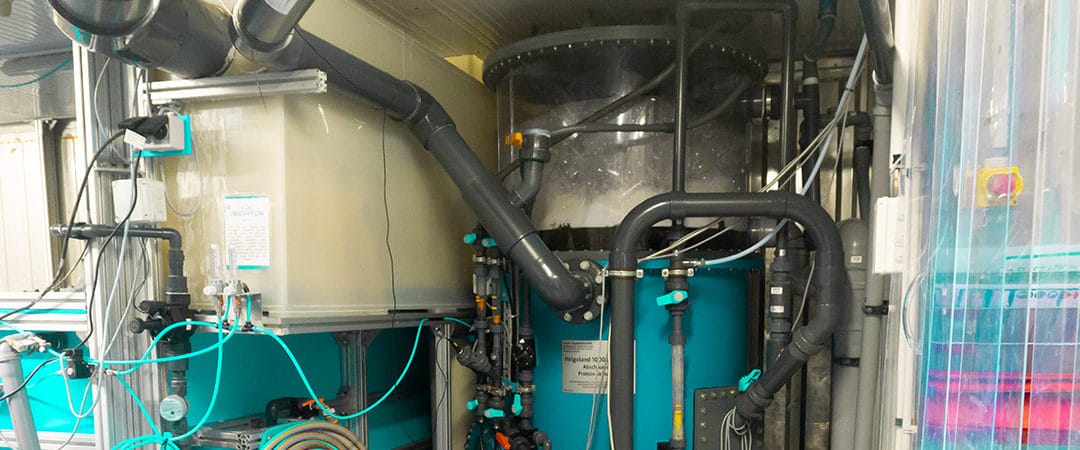

Protein skimmers in recirculation systems
Effective water treatment in aquaculture cannot be done without the work of bacteria, because in specially built biofilters they often convert toxic excrements of the fish into animal and environmentally friendly substances. However, if bacteria are present in larger numbers in the bearing tank, they can cause undesirable side effects. Therefore, in closed recirculation systems, a protein skimmer is used in addition to biological filters.

First step in water treatment: The drum filter
Almost everyone has done this at least once in their own four walls: For example, you use a sieve and water and simply rinse the dirt away, leaving only the clean salad at the end. This is a type of mechanical cleaning that almost everyone uses regularly. In order to achieve a similar effect in a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS), a comparable filter option is used in a figurative sense: the drum filter, a cylindrical drum covered with a fine-mesh filter net. Learn more about this smart filter technology in our blog post!
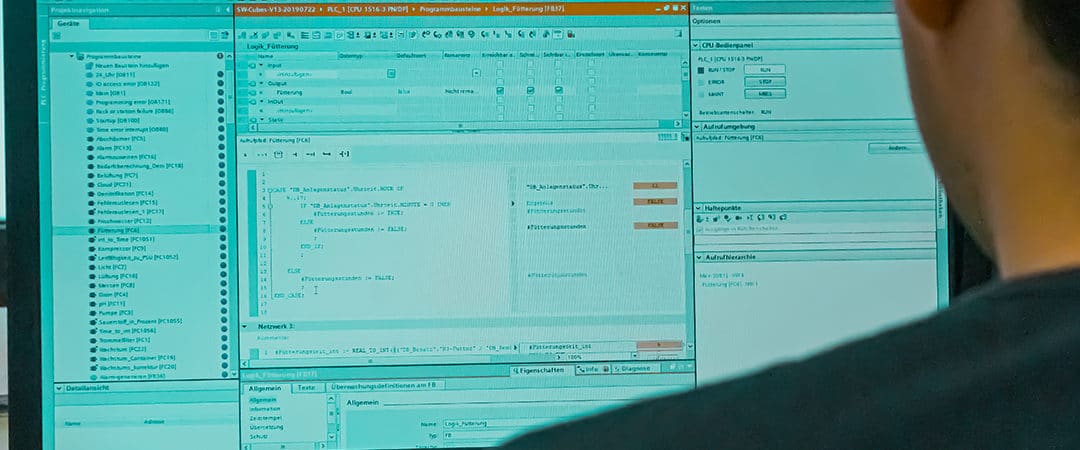
Automation of fish farming systems
The topic of automation is becoming more and more important, especially in today’s world. Especially in industry, where high productivity is always the goal and processes are increasingly digitalized (Industry 4.0), many different applications of automation can be found. In our blogpost we explain in detail, how programmable logic controllers can be used in recirculation systems and how processes and workload can be optimized.
Efficient oxygen input by flow pump
Each species of fish has its own preferences for perfect flow conditions: some fish species prefer permanent currents and „surf“ in them, others only move to spawn in currents and others prefer to live in calm waters. The background is the oxygen demand that every…

Sedimentation in detail
Sedimentation is part of the water filtration in our circulation system. But what exactly is it responsible for and how does it work? In the blog post we go into more detail about the component and explain how water loss in recirculation systems can be minimized through smart recovery.
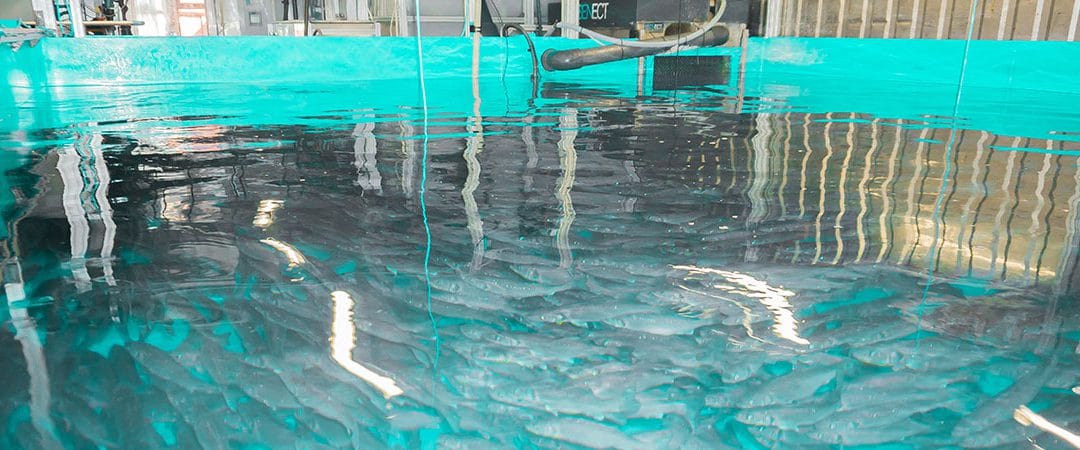

Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS)
The cultivation of fish on land has been greatly optimized over the past centuries. In particular, the closed recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) has now established itself alongside traditional aquaculture methods such as pond systems, net cages and flow-through systems. In order to get a concrete overview of the differences between these methods, the characteristics of technological recirculating aquaculture systems are compared with traditional breeding methods. In addition, the SEAWATER Cube is used to explain the construction of an innovative closed recirculation system in detail in the individual process steps.
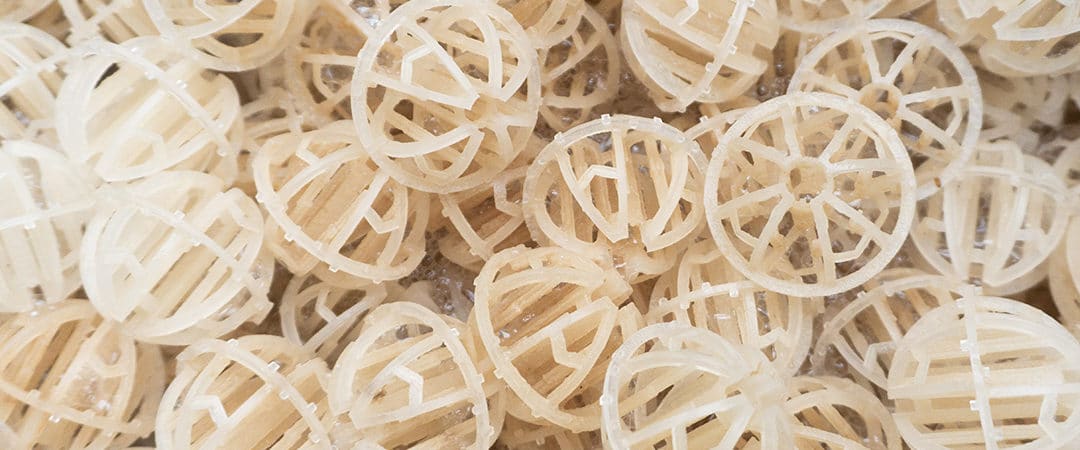

Microbiology and technology of denitrification
In closed aquaculture – e.g. in systems with a water exchange of less than 10% per day – the use of denitrification is essential. Denitrification converts the nitrate (NO3) converted from fish excrements (ammonium/ammonia) during nitrification with the help of special bacteria, the so-called denitrifiers. Molecular nitrogen (N2) is formed from the nitrate in the absence of oxygen, which then escapes from the plant in gaseous form. We explain the most important details about denitrification in aquaculture systems.
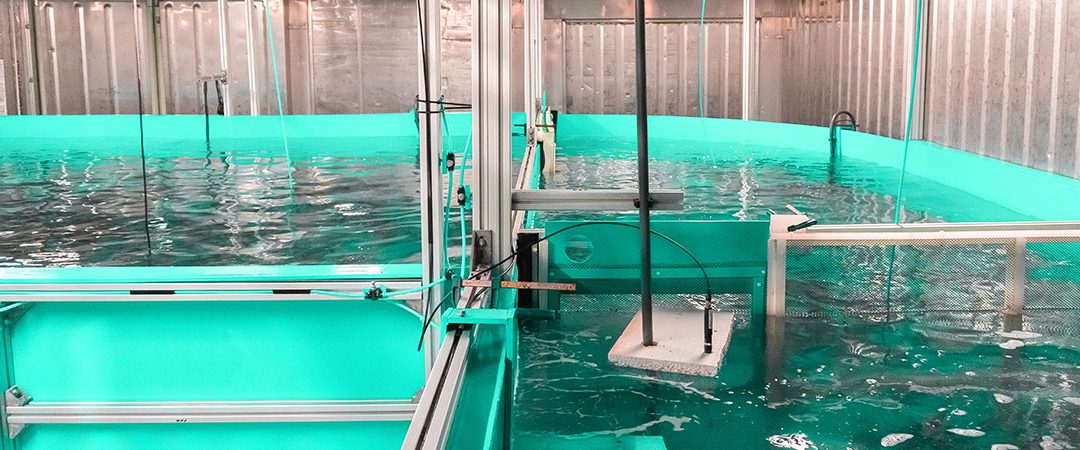

Fish farming tank
The central component of an aquaculture facility is the fish farming tank. Its dimensions and capacity influence both which fish species can be held and the annual production volume. But what are the different types of fish tanks and which species are kept in our facility? In our blog post we give a short overview.

Cohort model
Already in the Middle Ages, monks divided their carp ponds into sections of different sizes. Even today, the separation of the farmed fish into so-called cohorts is still used. But what is this division actually good for? The basic idea behind the cohort model is to…